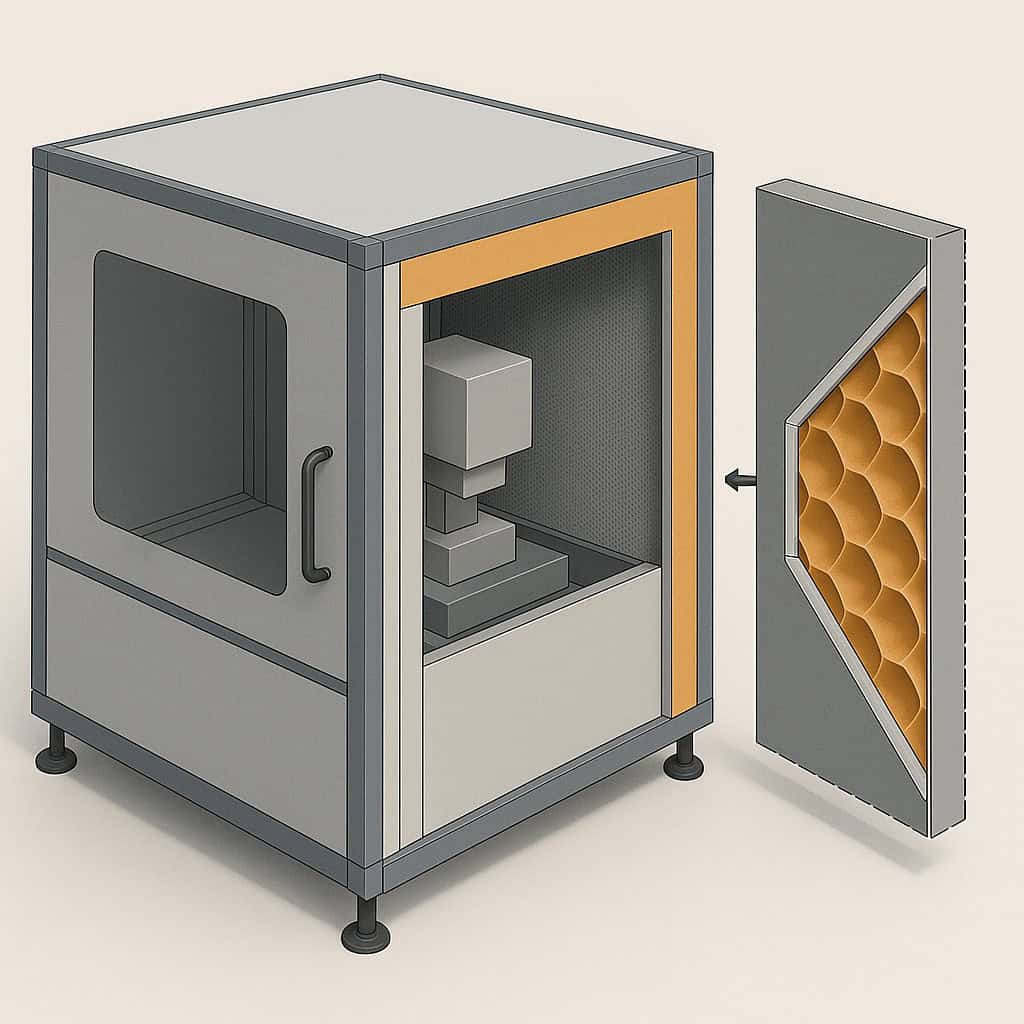
Technical problem definition
Heat shields must be able to withstand high temperatures and dynamic loads without losing their structural integrity. Conventional sheets have a low energy absorption capacity and are susceptible to local stress peaks that can lead to failure. The aim is a structure with:
- High specific stiffness (E/ρ)
- Uniform stress distribution despite high temperature stress
- Good energy absorption in the event of impacts from foreign bodies
- Minimum weight
The challenge
An effective design requires a balance between strength, dimensional stability and weight. Conventional manufacturing methods are usually material and energy intensive. Especially for applications in the aerospace, automotive and other vehicle construction sectors, a reduction in structural mass combined with increased functional integration is essential.
Solution and result
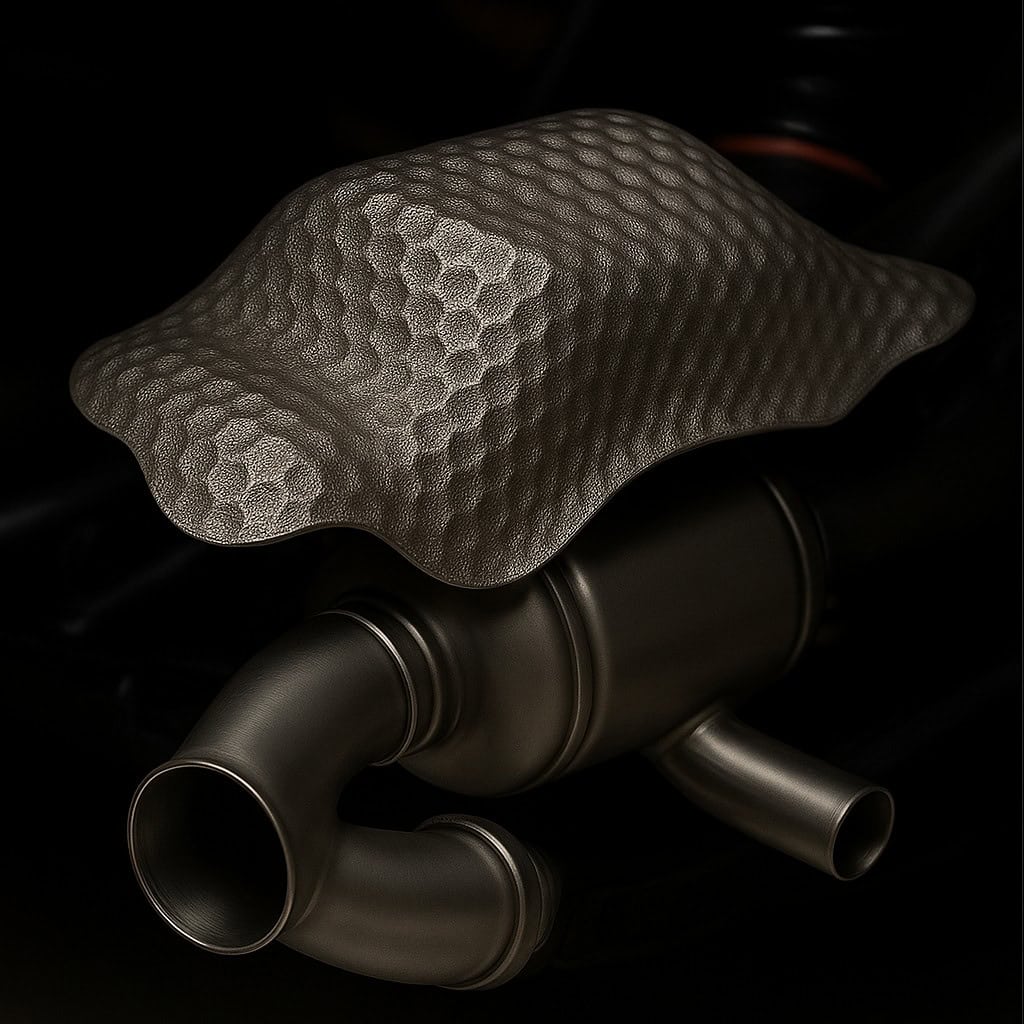
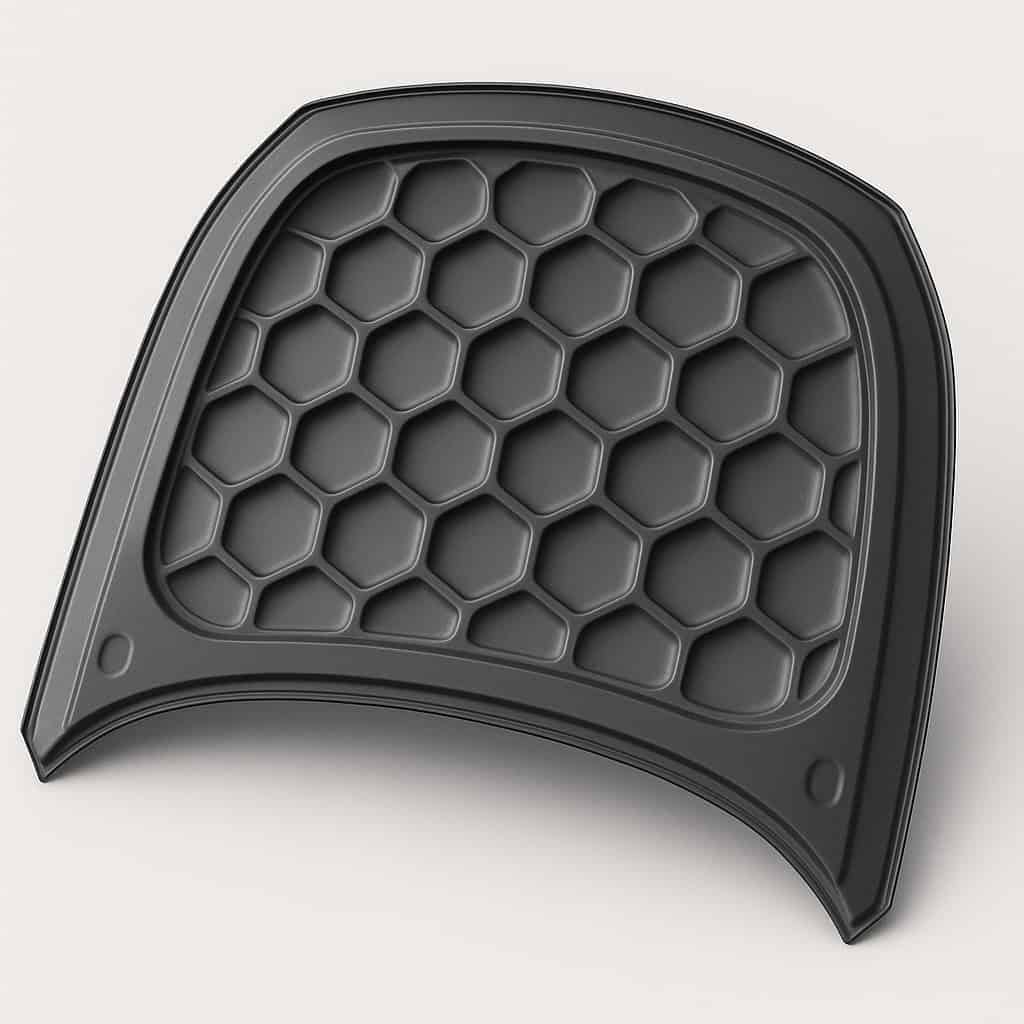
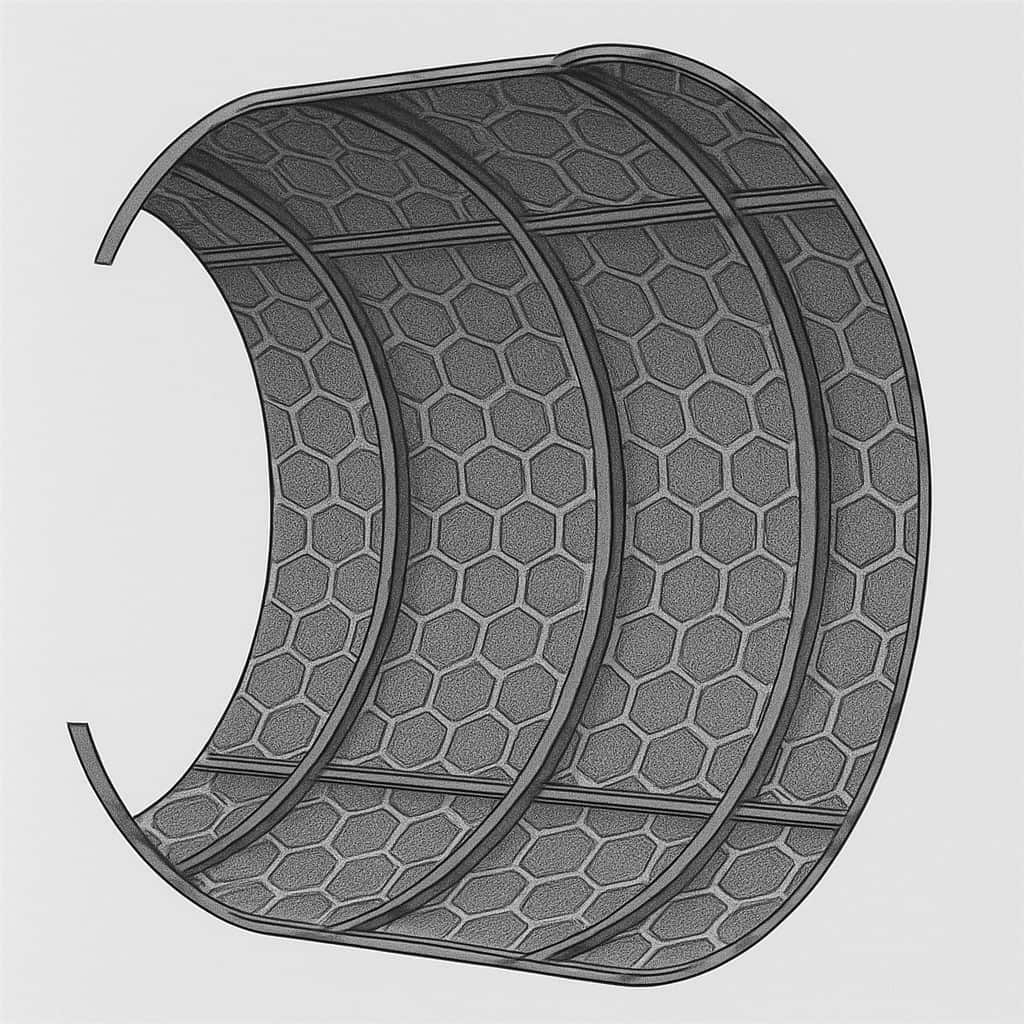
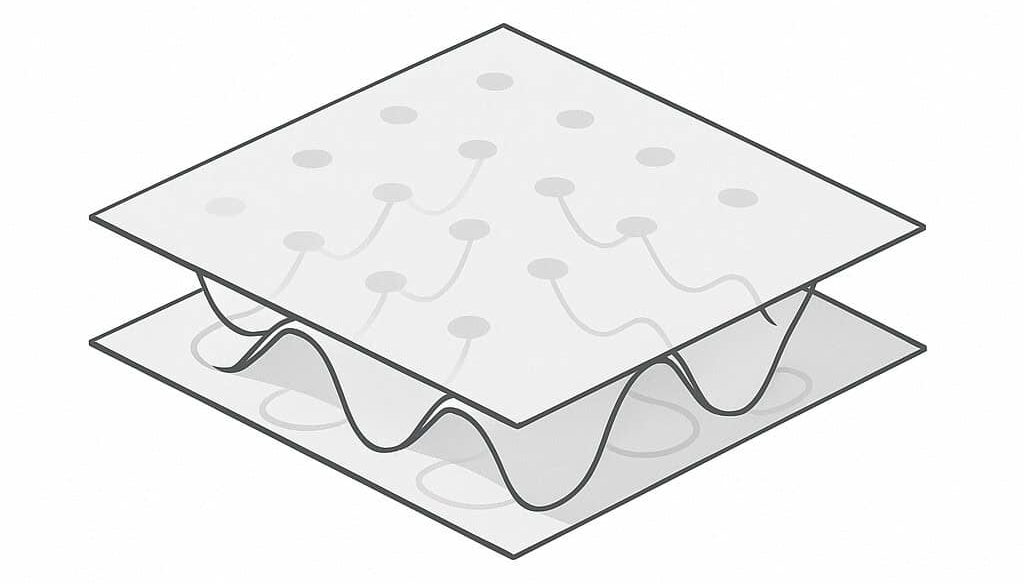
The solution lies in the application of camber structuring according to the bionic principle. This self-organizing forming process produces structured semi-finished sheet metal products with the following properties:
- 7 times the bending stiffness of smooth sheet metal (3-point bending test)
- Isotropic stiffness in two directions
- High energy absorption under impact load (DeepHEX structure)
- Minimal local hardening → good forming reserves
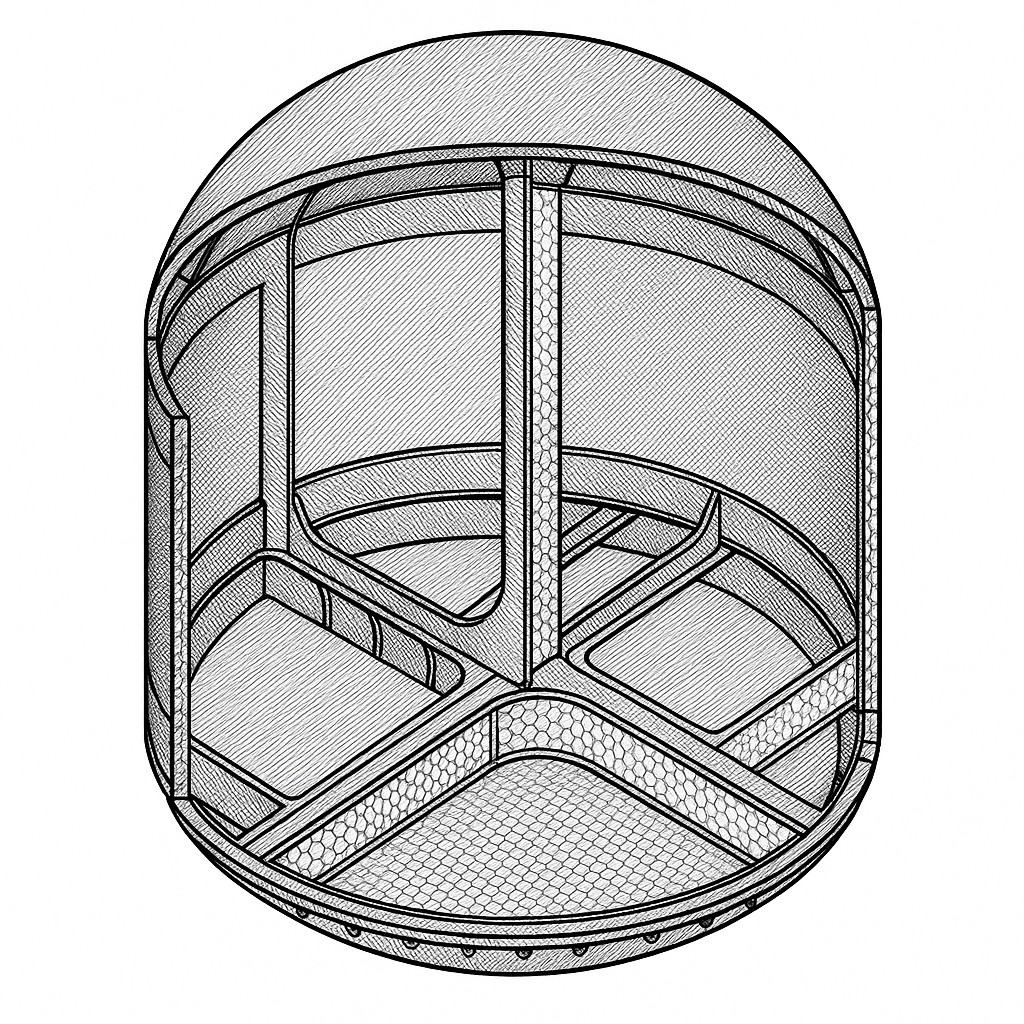
Arch-structured, thin-walled sheets are examined in detail using a coupled FE-based thermomechanical topographical/topological analysis in accordance with customer requirements in order to work out minimum wall thicknesses and shaping in the installation space. Preliminary investigations have shown that the mass of the heat protection plates could be reduced by up to 60 % compared to conventional plates, depending on the initial situation. At the same time, the mechanical characteristics are improved.